Structure of Body Organization
Structure of Body Organization
- Capture outlets
- Body cavities
- Directional terminology
- Body plans
- Abdominal regions
- Abdominopelvic Quadrants
- New routes suffix and prefix
Body Cavities
- Dorsal cavity
- venter cavity
- cranial cavity
- Vertebral cavity
- Abdominal cavity
- Pelvic cavity
- thoracic cavity

When you study the body cavities think of backspace . The backspace has empty spaces called poaches . Some are big, Some are small. The body has empty spaces inside it has well . But they are not called pouches they are called cavities.
The body has two main cavities : The dorsal and the ventral. The dorsal cavity is also called the posterior cavity, because it is at the back of the body. posterior refers to the back. The ventral cavity is also call the anterior cavity , Because it is at the Front of the body. anterior refers to the front . Each of these cavities has further subdivision .
Dorsal Cavity
The Dorsal Cavity is subdivided into two parts the Cranial cavity And vertebral cavity. The cranial cavity is inside the skull. The brain is contained in the Cranial Cavity. The vertebral cavity is inside the vertebral column, or spine. the spinal cord (a group of nervous) is continue in the vertebral cavity.
Ventral Cavity
The ventral cavity contains many internal organs including The heart , lungs, kidneys, digestive organs, and others, These internal organs are also called Viscera. A Large muscle called the diaphragm device the ventral cavity into upper and lower cavities. the upper cavity is called the thoracic cavity. The lower cavity is the abdominopelvic cavity.
The thoracic cavity contains the heart and lungs. The abdominiopelvic cavities is divided into two smaller cavities the abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity. The abdominal cavity is about the pelvic cavity. It contains organs such as the liver, intestines, stomach, and kidneys. The pelvic cavity contains some reparative organs the urinary bladder and part of the intestine.
In Brief :
- The dorsal Cavity is subdivided into the cranial and Vertebral cavities.
- The ventral cavity is subdivided into the thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavities.
Directional Terminology
Anatomical Position
If you are going To tell Someone how to get somewhere you both need to understand what is east , west , north and south means. These words are called directional terms because they tell direction.
In healthcare we need directional terms that will accurately Describe where particular body structure are located. The problem is that bodies can move. You can lie on your back, your front, or either side. You can stand or sit. A change in position would change the meaning of the directional terms.
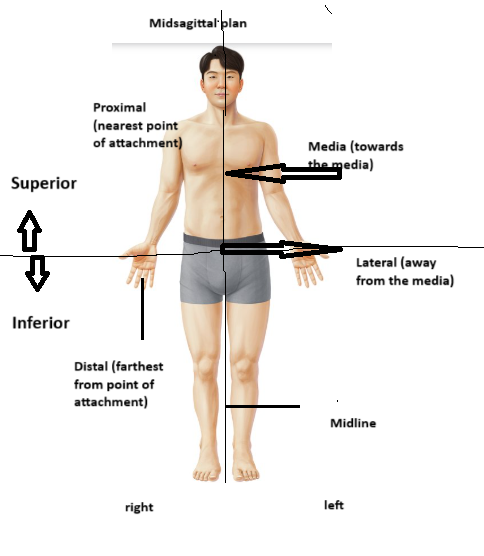
There is a simply solution to this problem. Everyone using direction terminology in health care must think of body in a standard position. This is known as the anatomical position. It is illustrated below figure , The body is standing erect , arms by the side , with head, palms, and feet facing forward. All directional terms assume that the body is in this position.
Directional Terms
As stated Above we need directional terms to describe the position of body parts , particularly in relation to each other. Directional terms are also useful in communicating the location of disease when they appear in the body.

For example the terms “superior” and “inferior” are grouped because they are opposites superior means “about” and inferior means “below” .
| Directional Term | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| superior | above | The head is superior to the neck. |
| inferior | below | The neck is inferior to the head . |
| ventral (anterior) | front | The thoracic cavity is anterior to the vertebral cavity. |
| dorsal | back | The ventral cavity is posterior to the thoracic cavity. |
| medial | towards the midline of the body | The big toe is medial to the small toe. |
| lateral | away from the midline of the body | The small toe is lateral to the big toe. |
| proximal | 1. nearest to the point of attachment to to the trunk. | The elbow is proximal to wrist. |
| distal | farthest from the point of attachment to the trunk | The knee is distal to the hip. |
| superficial | near the surface of the body | The skin is superficial muscle . |
| deep | away from the surface of the body | The muscle is deep to skin |
| supine | lying on the back , face up | During an operation on the abdomen, the patient is placed in the prone potion. |
| planter | bottom of the foot; solo of the foot | Planter warts are on the sole of the foot |
| dorsum | top of the foot | The dorsum of the foot is the top of the foot. |
| Plane | Definition |
|---|---|
| frontal; corona | structure into anterior and posterior portions |
| sagittal | separate a structure into right and left portions, if the sagittal section |
| transverse; horizontal | separates a structure in to superior and inferior portion. |
Abdominopelvic Regions
- right hypochondhriac region
- epigastric region
- left hypochondhriac region
- right lumbar region
- umbilical region
- left lumbar region
- right inguinal or iliac region
- hypogastric region
- left inguinal or iliac region
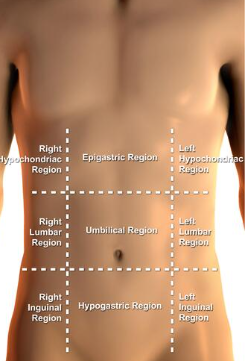
The abdominopelvic area can be divided into nine Regions , Each region is given a name and each region contains specific organs. When a patient Has Pain in the abdominopelvic area, The name of Region is used to communicate the exact location of the pain. For example a physical may say “The pain is in the right iliac region” This means the pain is located in the patient’s right hip area.
When you were looking at a Illustrations, be careful to remember that the right and left abdominal regions refer to the patient’s right or left not yours.
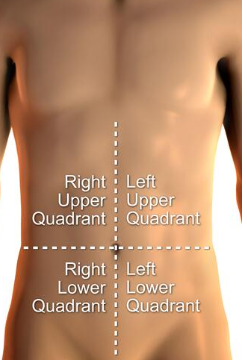
Abdominopelvic Quadrants
1.right upper quadrant (RUQ)
2.left upper quadrant (LUQ)
3.right lower quadrant (RLQ)
4.left lower quadrant (LLQ)
The abdominopelvic area can also be divided into four area called quadrants .
New Roots, Suffixes, and Prefixes
| ROOT | MEANING |
|---|---|
| anter /o | front |
| ili/o | hip |
| dors/o | back |
| infer/o | below; downward |
| inguin/o | groin |
| medi/o | middle |
| poster/o | back |
| proxim/o | near |
| super /o | above; toward the head |
| ventro/o | front |
| vertebr/o | vertebra (any of 33 bones making up the spine) |
Suffixes
- SUFFIX MEANING (-ac&-al) (pertaining) Terms Terms Analysis Definition
- iliac ili/o = hip pertaining to hip
- abdominal abdomin/o=abdomen pertaining to abdomen
- cranial crani/o = skull pertaining to skull
- dorsal dors/o =back pertaining to the back of the body or organ ; poster
- inguinal inguin/o= groin (the groin is the fold pertaining to the groin between the thigh and lower abdomen)
- lateral lateral/o= side pertaining to the side
- medial medi/o= middle pertaining to the middle
- proximal proxim/o= near; close to pertaining to something being near a specific point
- spinal spin/o= spine; vertebral column pertaining to the spine
- ventral ventr/o= front pertaining to any one of the 33 bone making up the spine
- visceral viscer/o = internal organs pertaining to the internal organs
- epigastric epi- = above; upon pertaining to upon the stomach ,,,, gastro/o =stomach
- pelvic pelv/o = pelvis pertaining to the pelvis
- thoracic thorac/o= chest pertaining to the chest
- anterior anter/o=front pertaining to the front
- inferior infer/o= below; downward pertaining to below or in a downward position;
- posterior poster/ o =back pertaining to the back of the body or an organ
- superior super/ o= above; toward the head pertaining to above or toward the head.