1.The Integumentary System
1.The Integumentary System
Chapter outline
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue
- Accessory structure
- Learning the times
- New Roots, Suffixes, and Prefixes
- Pathology
Introduction
The body is covered with skin ny and hair together with a gland formed in the skin they make up the integumentary system. it gets its name from the latin word integumentum meaning ” covering ”
The skin is an organ, just like the heart and lungs, it is the largest organ in the body, The skin has two layer the outer layer (epidermis) helps prevent harm full substances from entering the body. The inner layer (dermis) contains glands that secrete importance substance, nerves that carry electrical impulse and blood vessels that help keep the body at the right temperature.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue
1.epidermis
2.dermis
3.subcutaneous tissue
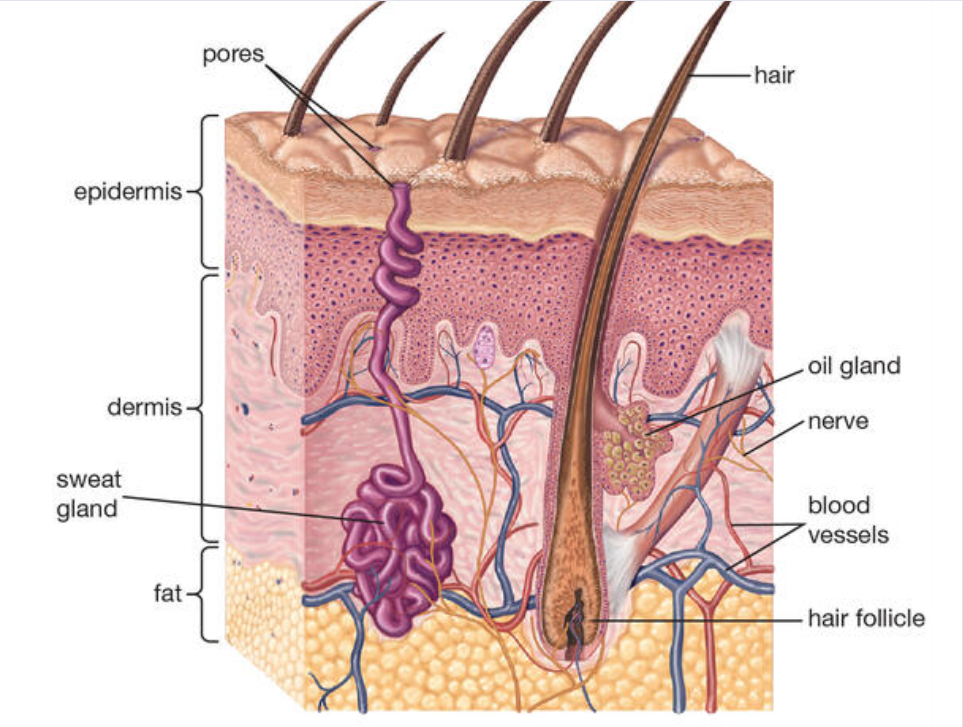
The outer layer is part of the skin and is called the epitomes. underneath it is another layer of skin called the dermis. Underneath the dermis is a fatty layer called Subcutaneous tissue. It is not part of skin. The subcutaneous tissue attaches the skin to muscle close to the surface.
In Brief :
- Epidermis is the outer layer of skin.
- The dermis is under the epidermis
- Subcutaneous tissue is under the dermis
Epidermis
The epidermis is an organ made of tissue called epithelium. The cells are called epithelial cells. The epidermis is a protective covering over the entire body and line body cavities and covers organs.
The epidermic protects us from the sun’s rays by producing melanin. Melanin is produced by the cells in the epidemic called melanocytes. Darker Skin has more melanocytes than lighter skin. Skin with more melanin has better product from the sun. Skin also protects by keeping infectious materials from entering the body and it waterproofs the body and prevents fluid loss.
Dermis
- 1.sebaceous
- 2.nerve
- sweat gland
- vein
- artery
The Dermis is made of connective tissue. A major component of connective tissue is collagen, which makes the skin flexibly and strong.
If you are cut down to this layer you will bleed, The blood vessels supply nutrients to the epidermis and dermis. They also help control body temperature.
The dermis also contains nerves, They give us sensations such as touch, pain, temperature, and pressure. Also in the dermis are glands and hair follicles. These parts are discussed below under the heading accessory structure.
In Brief : The organs located in the dermis are : blood vessel, nerves, glands, and hair follicles.
Subcutaneous Tissue
Subcutaneous tissue is deep to the dermis and composed of mostly adipose tissue it cells are called adipose adipocytes. Besides storing fat, this layer loosely connects the skin to the underlying muscles and products us from injury. It is also known as superficial facial facia. Fascia is connective tissue that holds parts together. In this case, it holds the skin to the muscles. It is called superficial fascia because the subcutaneous tissue is closer to the surface of the body than the fascia surrounding the muscle.
Accessory Structures
Glands
There are glands in the dermis that secrete substances necessary for skin function. Sebaceous glands secrete oil called sebum. It keep the skin and the hair soft and pliable .Sweat gland help regulate temperature by secreting sweat on to the surface of the skin. When the sweat evaporates, the skin cools, Specialized glands in the ear named ceruminous glands secrete cerumen, a waxy substance that helps prevent bacterial infection.
Hair Follicles
There are also hair follicles in the dermis. They grow the hairs that covers our skin in certain places. When hair is lost on top of the head, the person is said to be bald. The medical word for bald is alopecia .The opposite, the presence of excessive body and facial hair , especially in women, is called hirsutism.
Nails
Nails are protective covering on the ends of fingers and toes. nails are epithelial cells that have been hardened. At the base of each nail is the white. half- moon shaped lunula. The word luna means moon. It is from the lunula that the nail grows. Other anatomical structure are the nail bed and cuticle or eponychium.
In Brief
Accessory Structures
glands, hair, nails
Glands
sebaceous, sweat, ceruminous
Nails
includes lunula, nail bed , eponychium
| ROOT | MEANING |
|---|---|
| chem/o | drug |
| cry/o | cold |
| crypt/o | hidden |
| melan/o | black |
| myc/o | fungus |
| staphyl/o | resembling a bunch of grapes |
| strept/o | twisted |
| xer/o | dry |
| SUFFIX | MEANING |
| -cle | small |
| -edema | swelling |
| -ion | process |
| -ium | structure |
| -ose | pertaining to |
| -sis | condition |
| PREFIX | MEANING |
| tele- | distant |
| ROOT (Term) | (Term Analysis) | MEANING (Definition) |
|---|---|---|
| adipose | -ose = pertaining to | pertaining to fat |
| biopsy | opsy = to view | a procedure involving the removal of a piece of living tissue, |
| subcutaneous | sub = under -ous = pertaining | pertaining to under the skin |
| cyanosis | -sis = condition | bluish discoloration of skin |
| dermatitis | -its = inflammation | inflammation of the skin |
| dermatologist | -logist = one who specializes in the study of | one who specializes in the study of the skin and its diseases |
| hypodermic | -ic = pertaining to hypo- = under ; below | pertaining to under the skin |
| erythema | "-a" is a noun ending | red discoloration of the skin |
| erythematous | -ous = pertaining to | pertaining to the skin |
| ketatosis | -osis = abnormal condition | any skin growth, such as a wart or callus, in which there is overgrowth or thickness of the skin. |
| lipedema | -osis = abnormal con | chronic abnormal condition that is characterized by the accumulation of fat and fluid in the tissues just under the skin of the hips and legs. |
| lipoma | -oma = tumor; mass | tumor or mass containing fat |
| liposuction | suction = process of aspirating or withdrawing | withdrawal of fat from the subcutaneous tissue |
| necrotic tissue | -itc = pertaining to | pertaining to the death of tissues. Ex decubitus ulcer |
| eponychium | -ium = structure epi- = upon | structure upon the nail; cuticle |
| onychocryptosis | -osis = abnormal condition | fungal infection of the nail; also know as tinea unguium |
| pediculosis | -osis = abnormal condition | infestation with lice |
| abrasion | -ion = process ab-= away from | scraping away of the superficial layers your skin on the cement results in an abrasion. Also know as an excoriation |
| subungual | -al = pertaining to sub- = under | pertaining to under the nail |
| vesicle | -cle= small | a blister; a small elevation on the skin filled with clear fluid |
| staphylococcus | staphy/o = resembling a bunch of grapes | berry-shaped bacteria growing in small clusters, like grapes |
| streptococcus | strept/o = resembling twisted | berry- shaped bacteria growing in twisted chains |
| melanocyte | melan/o = black | cells producing melanin |
| scleroderma | scler/o = hard | skin becomes hard and swollen because the connective tissues become thick and hard |
| xeroderma | xer/o = dry | extreme dryness of the skin |
| chemotherapy | chemo/o = drugs | treatment with drugs. Usually refers to the use of drugs on cancer patient |
| cryotherapy | cry/o = cold | destruction of unwanted tissue, such as warts, by freezing with liquid nitrogen. The freezing destroys the tissue. |
| laser therapy | laser = intense beam of light | removal of skin lesion such as birth marks or tattoos using an intense beam of light called a laser. lasers are also used in cosmetic surgeries. |
| radiotherapy | radio/o = x- rays | the use of radiation to treat disease, usually cancer radiotherapy is not used to diagnose disease. |
| teletherapy | tele- = distant | radiation treatment applied to a tumor at a distance from the body. |
Pathology
Burns
A burn is an Injury to the skin caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation, Burns can be described by how deep the burn is and by the area of skin burned.